About 80% of the population is affected by skin fungi. Due to the increased density and sweating, mycoses are more affected by the skin of the feet. The fungal infection is manifested by scaling and itching, but can also be asymptomatic, causing only the appearance of seals (calluses, calluses - hyperkeratosis on the heels and arches of the feet). If left untreated, the infection spreads. The patient can infect others, spread germs throughout his body.
Where did the fungus come from

Fungal microorganisms love a humid and warm environment and an abundance of nutrients. As a "shelter" they use thick skin, prone to increased secretion of fat and sweat.
Human feet - always act as a breeding ground for mycobacteria, and poor quality socks and shoes contribute to this.
You can get infected in a public place - on the beach, in the sauna, in the pool. You can bring the infection when you try on new shoes, because the day before, a person with athlete's foot can measure it.
Some internal factors also increase the susceptibility to fungi:
- Weakness of immunity - fungi reject the body's defenses when they are weakened, microorganisms more easily penetrate the skin;
- endocrine disorders - diabetes mellitus and hormonal imbalance change the composition of skin secretions, turning them into a breeding ground for bacteria;
- resistant injuries - cracks, abrasions, scratches and punctures can be the door to the fungus;
- lack of hygiene - poor foot washing, the use of dirty socks and airtight shoes contribute to fungal invasions of the limbs.
Infection from a close person is also possible - if there is a patient or carrier of the fungus in the house with an asymptomatic course of the disease. Disputes about pathogenic microorganisms spread in household appliances, personal belongings, sex (if the patient moves barefoot). When washing the belongings of all residents of the house, mycobacteria get on the clothes of healthy family members, they can provoke mycosis not only on the legs but also on other parts of the body (in the folds, groin, hairy areas of the body).
Why do fungi appear between the fingers
Interdigital fungus is a special clinical form of mycosis of the feet. Doctors call it intertriginous. In this course, the skin is affected between 3 and 4 or 4 and 5 fingers. Often the pathological process starts from one limb and eventually spreads to a healthy one.
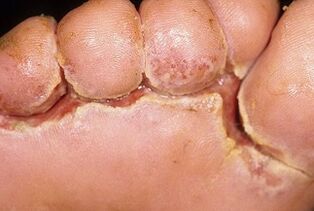
Mycosis begins with cracking of the skin between the toes or at the base of the phalanx of the foot. The size of the injury can be from 2-3 mm to 1 cm. The intensity of the symptoms depends on the area of the wound - the greater the damage, the stronger the pain. During the appearance of the crack, a person experiences a slight discomfort when walking, which increases with hygienic procedures.
Unlike other injuries, the crack does not heal on its own. It becomes inflamed, secretes exudate. The surface between the fingers becomes wet, which further contributes to the spread of the fungus in larger areas of the skin. "Fringe" appears around the injury - it's steam, peeled skin. The peeling is quite thick, attempts to remove it with your fingers end in injuries to healthy areas of the skin. Persistent peeling appears around the lesion. It can be lamellar or floury. The scales are silvery, white, yellowish. These characteristics depend on the strain of the fungus that infects the skin. After the crack has healed, the intriguing form of mycosis turns into squamous cell carcinoma - it manifests itself as extensive dry areas on the foot, with an abundance of exfoliated scales. The surface can be glossy or woven.
What to do with fungal symptoms
If you have a crack between your fingers, surrounded by sagging skin, you should definitely visit a dermatologist. The specialist will perform an examination, will determine the symptoms not only at the site of injury, but also on other parts of the limb.
The diagnosis cannot be made solely on the basis of symptoms. Microscopic examination of the scraping of the skin from the foot will be required to confirm the fungus. In the case of resistant mycosis, it is supplemented by PCR analysis or culture inoculation to determine the type of pathogen and its susceptibility to fungicidal drugs.
In advanced cases of fungus or extensive lesions of the dermis, systemic medications will be needed. Due to the likelihood of hepato- and nephrotoxic effects of such drugs, the patient should undergo blood and urine tests. Based on their results, the specialist assesses the function of vital organs, chooses a treatment regimen with systemic antifungals.
Self-medication for fungal infections of the feet is permissible only in the early stages. You can deal with topical medications that do not give systemic side effects.
Effective remedies against fungus between the fingers
The characteristics of the therapy depend on the individual patient's data, the degree of mycosis, the area of the lesion, the presence of a secondary infection or the resistance of the pathogen.
Systemic drugs
To speed up treatment and complete it, doctors prescribe antifungal drugs in the form of tablets or capsules.
When treated with drugs with systemic action, it is undesirable to consume alcohol, fatty foods and other foods that create a burden on the liver. If the infection has spread to the nails from the interdigital space, you will need to use antifungals for a longer time.
Local remedies
Medications on a moderately oily or non-greasy basis (creams, solutions) are prescribed for the treatment of interdigital fungus. Ointments can be used only in the initial stage, when it is necessary to soften the skin for rapid healing of lesions. Along the way, antifungal drugs can be prescribed remedies and antiseptics. They accelerate the regeneration process and further soften rough skin.
For the treatment of foot fungus, external agents with broad-spectrum fungicidal components are prescribed. Ideal for products based on:
- terbinafine;
- clotrimazole;
- ketoconazole;
- econazole;
- naftifine.
The price does not affect the success of treatment, it is important to choose the right active ingredient of the drug.
Creams and solutions are applied to the skin 1-2 times a day after hygienic procedures. After processing, the product can be completely absorbed and wear cotton socks. In parallel, it is necessary to disinfect shoes every 3-7 days. Fungicide sprays are used for this purpose. It is necessary to regularly change socks, underwear, towels. It is necessary to wash used items at elevated temperatures separately from other accessories of the patient and his family members.
In trichophytosis and microsporia, doctors recommend special treatment regimens. For example, treatment with iodine solution in the morning and sulfur, sulfur-tar or salicylic ointment in the evening.
Folk remedies
You can not treat fungus only by folk methods. In addition to medications, baths are allowed. If your doctor has recommended the use of home-made ointments or formulations, they should be used separately from the pharmaceutical preparations. For example, in the morning and evening use ready-made medicine, and in the afternoon - homemade ointment. The most popular methods of treating fungus among humans:
- baths with oak bark- make a large volume of broth from oak bark (6 tablespoons per 1 liter), dilute in half with clean water, take baths for 15 minutes a day;
- with sea salt- prepare a strong solution of sea salt, take a bath for 10 minutes, do not wash off the salt, put on cotton socks immediately after the procedure;
- with soda- dilute a tablespoon of baking soda in 1 liter of water, take a bath for 15 minutes, after wiping apply pharmaceutical antifungals;
- egg ointment- 1 chicken egg mixed with a tablespoon of oil and vinegar, mix until smooth, apply for 3-4 hours under the bag, wash with water;
- Tea tree- the areas affected by the fungus are lubricated abundantly with tea tree essential oil, washed off after 3 hours, in case of sensitivity the oil is diluted in half with neutral fats.
Rapid healing of the fungus is facilitated by the rejection of sweets, alcohol, fatty foods. The patient's diet should include plenty of vegetables, fermented dairy products, whole grains.
To prevent the appearance of fungus on your feet and between your toes, you need to take good care of your foot hygiene. When visiting public places, avoid walking barefoot, use fungicides - any antifungal ointments or sprays are applied after a shower. New shoes should only be measured in new socks; you should not give your slippers to anyone.
























